
Molecular Descriptors For Cheminformatics Pdf Free
The MOLE db - Molecular Descriptors Data Base is a free on-line database constituted of 1124 molecular descriptors calculated on 234773 molecules. This data base is intended as a research and teaching tool and basically allows the researcher to: a) search for a specific group of molecules and analyse the corresponding values of molecular descriptors b) save in an output file the values of a. Linking the Resource Description Framework to cheminformatics and proteochemometrics. Authors; Authors and affiliations. Calculated molecular descriptors can also be added to RDF documents for molecular structures. Precompetitive preclinical ADME/Tox data: set it free on the web to facilitate computational model building and assist drug.
Results The work presented here focuses on linking RDF approaches to existing molecular chemometrics fields, including cheminformatics, QSAR modeling and proteochemometrics. Applications are presented that link RDF technologies to methods from statistics and cheminformatics, including data aggregation, visualization, chemical identification, and property prediction. They demonstrate how this can be done using various existing RDF standards and cheminformatics libraries. For example, we show how IC 50 and K i values are modeled for a number of biological targets using data from the ChEMBL database. Conclusions We have shown that existing RDF standards can suitably be integrated into existing molecular chemometrics methods.
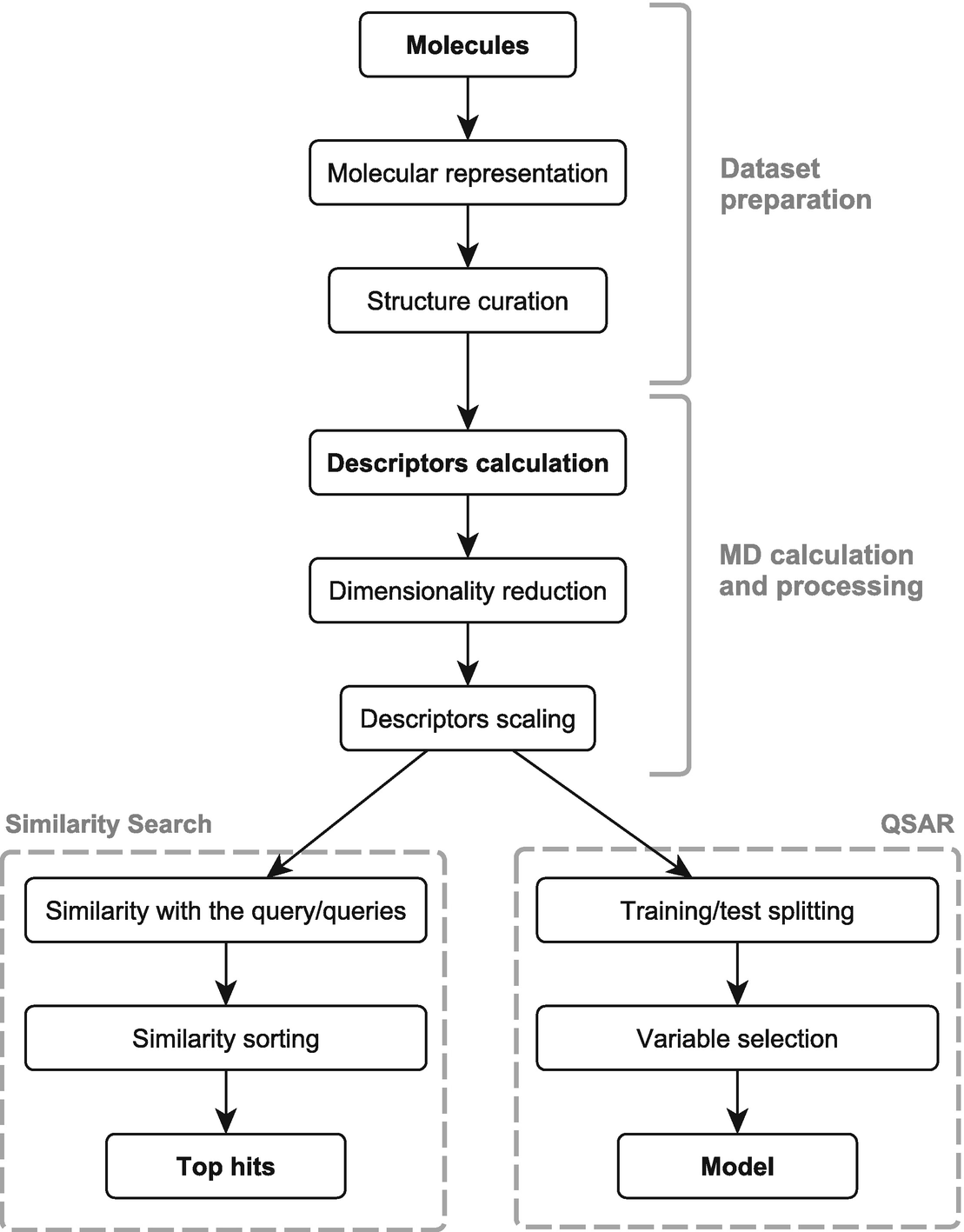
Platforms that unite these technologies, like Bioclipse, makes this even simpler and more transparent. Being able to create and share workflows that integrate data aggregation and analysis (visual and statistical) is beneficial to interoperability and reproducibility. The current work shows that RDF approaches are sufficiently powerful to support molecular chemometrics workflows.
Molecular chemometrics is the field that finds patterns in molecular information, combining methods from statistics, machine learning, and cheminformatics. We argued before that semantic web technologies are important for lossless exchange of data [ ], but it should also be noted that molecular properties are not well described by semantic web technologies alone; similarity of molecular structures is not easily captured by triples, but are required for pattern recognition. Therefore, we will focus in this paper on the interplay between the two kinds of knowledge representation. Sony vaio updates downloads.
Past research in molecular chemometrics has focused mostly on the development and use of statistics and cheminformatics, but semantic technolgies are equally important: the success of the statistical modeling depends very much on the setting up of proper input, as well as the ability to validate the created models against independent information sources afterwards, numerically [ ], as well as visually [ ]. This requires accurate and meaningful annotation of the data, which reduce the chance of errors introduced by the processes. This need has been recently met in chemistry by the Chemical Markup Language (CML) [,, ]. CML, however, does not formalize ontologies into the standard, though it does have mechanisms to validate dictionary references.